In the expansive world of cannabis, you may have heard about THC, but today, let's delve into something a little less known: THC-a, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid. When asking, "What is THC-a?", it's essential to understand it as a precursor to the well-known compound THC, found naturally in the raw cannabis plant.
The importance of understanding THC-a (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) cannot be overstated. As the wellness industry continually evolves, the need for comprehensive knowledge about the compounds we are introducing to our bodies is paramount. Unveiling the properties, benefits, and uses of tetrahydrocannabinolic acid provides clarity and insight into its potential role in health and wellness.
Stay tuned as we journey through the backstory, potential benefits, and methods of consumption, ensuring you're well-informed about tetrahydrocannabinolic acid and its place in the cannabis world. Your adventure into the depths of THC-a begins now. Welcome to the exploration of "What is THC-a?"
Background Information about THC-a
In order to fully grasp the concept of THC-a (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid), it’s crucial to first understand cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in the marijuana plant that interact with cannabinoid receptors in the human body to create various effects. There are numerous major cannabinoid receptors, each with its own unique properties and effects.
Explanation of Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids work by interacting with our body's endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex cell-signaling system that plays a key role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including sleep, mood, appetite, and memory. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are the most well-known cannabinoids, but THC-a is also a significant compound in a raw cannabis plant.
History and Discovery of THC-a
Exploring the history of THC-a, it's evident that this compound has not been as widely studied or understood compared to THC and CBD. THC-a was first discovered as part of the extensive research into cannabis and its compounds throughout the 20th century. It is the acidic precursor to THC and is found in the raw cannabis plant.
When cannabis is heated, through a process called decarboxylation, THC-a is converted into THC, the compound known for its psychoactive effects. Cannabis plants aren't automatically equipped with cannabinoids; they start out as cannabinoid acids. This understanding has led to a deeper exploration into the potential benefits and uses of THC-a in its unheated form. Scientists and researchers continue to investigate the health and wellness potential of THC-a, contributing to its growing prominence in the cannabis and wellness industry.
Understanding THC-a history and its progression is crucial to appreciating its potential impact on health and wellness. It emphasizes the importance of continued research into cannabinoids and their effects, shedding light on the many other compounds in cannabis that hold promise for therapeutic use.
With a clearer background on THC-a and cannabinoids as a whole, it’s easier to navigate the ongoing research and emerging information in the cannabis world. Stay engaged as the journey into understanding THC-a continues.
THC-a vs. THC
Navigating the intricate world of cannabis and its compounds, the distinction between THC and THC-a stands as a fundamental knowledge point for enthusiasts and curious minds alike. When comparing THCa vs THC, understanding the key differences is essential for making informed decisions regarding medical cannabis use and exploring its potential benefits.
The chemical structure of THCA is very similar to that of THC; the sole distinction between the two is the presence of an extra carboxyl group. The difference between THC and THCA lies in the presence of an additional carboxyl group. THCA is therefore the more acidic of the two compounds.
Differences Between THC and THC-a
Cannabis plants produce over one hundred distinct cannabinoids. One of the non-psychoactive cannabinoid that the cannabis plant produces in addition to CBD is called THCA, and it can be discovered in cannabis that has recently been harvested.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is a compound in cannabis known for its psychoactive effects. It’s what’s responsible for the “high” people experience when using cannabis. On the other hand, THC-a (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is a non-psychoactive compound found in raw and live cannabis plants.
One major difference is the state of the cannabis. Unlike THC, THC-a is present in freshly harvested cannabis and does not produce a "high". Only upon heating does THC-a transform into THC, unleashing the psychoactive properties that are commonly associated with cannabis consumption.
What do Psychoactive Effects mean?

THC is a psychoactive chemical whose psychoactive effects can influence the mind, affect emotions, and affect how aches are perceived. THC has drawn recreational users because of its advantages. But the psychoactive component of THC. However, it has strong medical advantages, like antibacterial traits and neuroprotective actions.
The Process of Decarboxylation

Delving into the transformation process, we encounter the term decarboxylation. It’s a crucial chemical reaction that activates the psychoactive properties of cannabis extracts. During decarboxylation, THC-a is heated, which removes a carboxylic acid group from the molecule and releases carbon dioxide. This process converts THC-a and creates THC, unlocking the psychoactive effects.
This is often why cannabis is smoked or baked (as in edibles), as the heat instigates the conversion from THC-a to THC, allowing users to experience the psychoactive effects.
Understanding the contrast between THC-a and THC and the essential process of decarboxylation provides a clearer, more comprehensive insight into the world of cannabis. Recognizing the distinctions allows for a more educated approach to its use, setting a foundation for exploration and discovery within the expanding realm of cannabis and its many compounds.
Potential Benefits of THC-a
As the scientific and medical communities continue to explore the properties of various cannabinoids, interest in THC-a (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) is steadily growing. Though research is in its nascent stages, early findings suggest that THC-a may offer a range of potential health benefits.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
One of the key potential benefits of THC-a is its anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a root cause of many health conditions, and compounds that can help reduce inflammation may have broad therapeutic applications.
Neuroprotective Effects

Preliminary studies indicate that THC-a could also have neuroprotective effects, potentially benefiting individuals with neurodegenerative disorders. Its ability to support brain health could be a significant boon as research progresses.
Non-Psychoactive

Unlike THC, THC-a is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t produce the “high” typically associated with cannabis use. This characteristic makes it a more attractive option for individuals seeking health benefits without the psychoactive effects.
Potential Therapeutic Uses
While more research is needed, early studies suggest that THC-a might be useful in managing pain, reducing anxiety, and supporting overall wellness. Its diverse range of potential applications holds promise for future therapeutic use.
Exploring Scientific Studies and Research
While comprehensive research on THC-a is still in its infancy, early studies are hinting at possible therapeutic benefits. Scientists are delving into understanding the ways in which THC-a interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, similar to other cannabinoids. This research is fundamental in uncovering the potential roles THC-a could play in health and well-being.
Therapeutic Uses of THC-a
Preliminary research and anecdotal evidence suggest that THC-a may hold promise in a variety of therapeutic applications. Some of the THC-a benefits being explored include anti-inflammatory properties, neuroprotective qualities, and potential to aid in immune system enhancement.
In addition to these, THC-a is also being investigated for its role in pain relief and reducing nausea or appetite loss, similar to THC and CBD. Although the research is ongoing, the findings thus far provide hope for future, more extensive studies to further confirm and understand the therapeutic benefits of THC-a.
Moving Forward with THC-a Benefits
In light of the emerging studies on THC-a benefits, it's crucial to approach this compound with an open yet discerning mind. Keeping abreast of the latest scientific findings and clinical trials will be key in understanding the full spectrum of benefits that THC-a may offer and helping individuals make informed decisions regarding its use.
Embracing the exploration of THC-a and its potential benefits signifies a step forward in the expanding field of cannabis research and holistic health solutions. As the journey continues, the anticipation of unearthing more about THC-a and its possible impact on health and wellness grows, underscoring the importance of continued research and discovery in this evolving arena.
How to Consume THC-a
Entering the world of cannabis compounds requires a foundational understanding of not just their potential benefits but also the appropriate methods for consumption. This is especially true for THC-a, a compound naturally present in raw cannabis. Unraveling the details and precautions for consuming THC-a ensures a safe and informed exploration into its potential.
Different Methods of Consumption
When it comes to consuming THC-a, it's fundamentally different from other cannabinoids, primarily because it's found in raw cannabis. The most direct method to consume THC-a is by using fresh cannabis leaves and flowers in juicing. This method allows cannabis consumers to intake THC-a without the intoxicating effects that come with decarboxylated THC.
Beyond juicing, THC-a is also available in other forms. Some manufacturers offer THC-a in tincture or capsule form, making it easier to consume as part of a daily wellness routine. These products are formulated to deliver the potential benefits of THC-a without the need for handling or juicing raw cannabis plants.
Precautions and Guidance for Consuming THC-a
Despite the various methods available for consuming THC-a, it’s vital to proceed with caution. It's crucial to start with a low dose to monitor individual body responses, adjusting as necessary under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Additionally, sourcing is paramount. Ensure that any THC-a products or raw cannabis used are obtained from reliable, reputable sources that adhere to industry standards and regulations. This ensures the quality and safety of the THC-a consumed, offering peace of mind alongside potential health benefits.
The Journey Continues: Consuming THC-a Safely
In the world of THC-a aka tetrahydrocannabinol acid, understanding the appropriate and safe methods for consumption stands as a cornerstone to fully realizing its potential benefits. Keeping abreast of the latest guidelines, research, and industry standards for consuming THC-a will ensure a positive, informed, and health-conscious experience in exploring this promising compound.
The conversation around consuming THC-a is continually growing and evolving, mirroring the exciting advancements and discoveries in the cannabis and holistic health world. Stay engaged, informed, and open to learning more as the journey unfolds in the world of THC-a and beyond.
Is THCa legal?
When exploring the realms of THC-a, understanding its legal standing is an essential component to consider. The global perspective on cannabis and its compounds is a vast tapestry, with legality varying significantly from one region to another. Let’s delve into the worldwide legal status of THC-a to garner a clearer picture of its accessibility and use across the globe.
Worldwide Legal Status of THC-a
Navigating the global legal framework, it's evident that the legal status of THC-a is still in a grey area in many regions. Given that THC-a is a precursor to THC, some jurisdictions categorize it similarly to other psychoactive cannabinoids, even though THC-a itself does not have psychoactive properties.
In the United States, for example, the legality of THC-a is complex. It's not explicitly listed as a controlled substance at the federal level, but once converted to THC (through the process of decarboxylation), it falls under the legal definition of synthetic THC, a schedule I controlled substance.
In other countries, the legal status can differ markedly. Some nations adopt a more lenient approach to all cannabinoids, while others have stringent regulations in place, restricting access and use of any cannabis-related compounds, including THC-a. It's crucial to thoroughly research and understand the specific legal guidelines pertaining to THC-a in your area or any area you plan to travel to.
Staying Informed About THC-a Legal Status
In the constantly evolving landscape of cannabis legislation, staying updated on the legal status of THC-a is paramount for those interested in exploring this compound. Engage with credible, up-to-date sources for legal information and consider consulting legal professionals for advice and clarity.
As the dialogue around cannabis and its compounds continues to grow worldwide, the legal perspectives on compounds like THC-a are likely to undergo changes. Being informed and aware of the legal status of THC-a in your region ensures a responsible and legally compliant approach to exploring or using this intriguing compound. Can THCA get you high?
No. When consumed by itself, the psychoactive substance THCA only causes high. Heat is required for the conversion of THCA into THC, which has a psychoactive effect such as that produced by smoking or vaporization.
Why does THC get you elevated and THCA doesn't?
Compared to THC molecules, THCA molecules are shaped differently. Cannabinoid molecules in CB1 cannot be bound by the THCA molecule. It is unable to connect to different THCA molecules. The main reasons for the enhanced effects of marijuana include interactions between tetrahydroxin molecules and the cannabinoid receptors. Cannabis creates a large number of cannabinoids, but only a tiny number of them are psychoactive.
Is a higher level of THC-a or THC better?
This is a question that doesn’t have a one-size-fits-all answer, as the “better” compound depends on the individual’s needs, health conditions, and goals. THC and THC-a serve different purposes and have distinct effects on the body, and they should be approached with these differences in mind. Below is a breakdown that might help inform this consideration:
THC vs THc-a
-
Psychoactive Effects: THC vs THC-a is psychoactive, meaning it produces a "high." This can be used for recreational purposes or therapeutically to help with issues like pain, insomnia, and stress.
-
Medicinal Uses: Medical marijuana, rich in THC, is used to relieve symptoms of various health conditions, including chronic pain, cancer, and AIDS.
-
Legal Restrictions: THC is classified as a controlled substance in many regions, and its use is regulated strictly.
Considerations:
-
Desired effects: If looking for psychoactive effects, THC would be the compound to consider.
-
Health goals: For symptom relief for specific health conditions, consult a healthcare professional to discuss the potential benefits and risks of THC.
-
Legal status: Ensure to understand the legal status of THC in your region and comply with all local regulations.
THC-a vs THC
-
Non-Psychoactive: THC-a is non-psychoactive in its natural state, meaning it does not produce a “high.”
-
Potential Health Benefits: Early research suggests that THC-a may have anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and other health-promoting properties.
-
Raw Consumption: THC-a is consumed in its raw form, often through juicing fresh cannabis leaves.
Considerations:
-
No “high”: If avoiding psychoactive effects, THC-a may be a more suitable choice.
-
Emerging research: Keep in mind that research on THC-a is in its early stages, and its full benefits and risks are not yet fully understood.
-
Consult a healthcare professional: Before starting any new supplement or wellness regimen, including THC-a, seek professional medical advice.
In essence, whether a higher level of THC-a or THC is "better" depends on individual factors, including the desired effects, health considerations, and legal status in your area. Both compounds have their own unique properties and potential benefits, and a healthcare professional can help guide informed, safe, and effective choices regarding their use.
THC-a: Can It Show Up in a Drug Test?
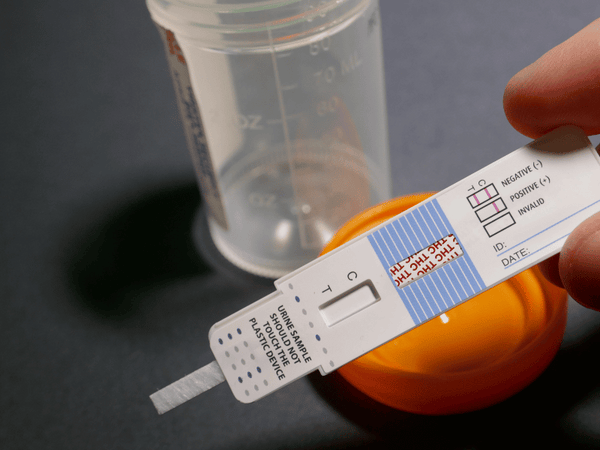
Navigating the world of drug testing can often bring a slew of questions, particularly around the detection of specific compounds like THC-a. It's crucial to understand how THC-a interacts with drug tests to ensure clarity and preparedness.
Understanding THC-a and Drug Tests
While THC-a is different from THC, questions still arise about its detectability in standard drug tests. The typical drug tests are designed to detect THC or THC metabolites, not THC-a specifically. However, depending on the sensitivity of the test and the consumption amount, it's not completely out of the realm of possibility for THC-a to be a concern.
Transformation into THC
One of the significant factors to consider is that THC-a can convert into THC, especially when exposed to heat. If someone consumes a substantial amount of THC-a and it undergoes decarboxylation, turning into THC, it could potentially be detected in a drug test.
Precautions and Guidance
As with all cannabis and cannabinoid-related products, it’s wise to err on the side of caution. Even though THC-a is non-psychoactive and different from THC, its potential conversion poses a consideration for drug testing.
Prior to Testing
1. Avoid Consumption: Refrain from consuming THC-a products leading up to a drug test.
2. Understand the Test: Know what the drug test is screening for. Some tests may be more sensitive than others.
3. Consult Professionals: If in doubt, seek advice from healthcare professionals for guidance.
How long does your body keep THCA?
It might be hard to figure out how long THCA stays in a person's body. Through a process called thymol breakdown, THC can be used to make drugs. THC can be found in the hair for 90 days and in urine for 30 days. Even though no one knows how long THCA stays in your body if you eat it raw, it may still cause an antipsychotic drug to be released.
Alive Market CBD+THC Gummies
Alive Market CBD+THC Gummies offer a unique blend of CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) in a convenient, tasty format. Designed to potentially provide therapeutic benefits, these gummies combine the relaxing properties of CBD with the euphoric effects of THC, offering users a balanced and enjoyable experience. When consumed, THC (like CBD and other cannabinoids) interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, which regulates a variety of physiological processes such as mood, appetite, and pain sensation.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricate world of THC-a demands a comprehensive, informed approach. Let's revisit the key points discussed to encapsulate our exploration of this unique cannabinoid:
-
Understanding THC-a
THC-a, a non-psychoactive compound, is the precursor to THC, found in raw cannabis. It's essential to understand its structure, function, and potential benefits, as these differ markedly from THC.
-
Background Information
Cannabinoids have a rich history, and the discovery of THC-a plays a pivotal role in continuing research on cannabis and its potential therapeutic uses.
-
THC-a vs. THC
Understanding the differences between THC and THC-a, especially the non-psychoactive nature of THC-a and the process of decarboxylation, is crucial for informed use and exploration.
-
Potential Benefits
Preliminary research is hinting at the potential benefits of THC-a, including anti-inflammatory properties and other health-promoting effects.
-
Consumption
It's vital to know the various methods of consumption and exercise due diligence and caution to ensure safe and effective use of THC-a.
-
Legal Status
The legal status of THC-a worldwide is a critical component, underscoring the importance of staying updated and compliant with legal guidelines and regulations.
-
Drug Testing
Understanding the potential for THC-a to show up in drug tests and the considerations surrounding this ensures preparedness and awareness.
In conclusion, while the exploration of THC-a is filled with promise and potential, it is paramount to approach this journey with an informed, cautious, and conscientious mindset. The world of cannabis and its compounds is continually evolving, and keeping abreast of the latest research, legal changes, and health information is essential for a safe and enriching experience with THC-a.
Your insights into the world of THC-a are crucial and welcome! Have any thoughts, questions, or personal experiences to share? Feel free to leave a comment below.
Do you think others could benefit from this information? Don’t hesitate to share this blog post within your community.
Stay connected and informed by continuing to engage with our platform. Your voice makes a significant impact on the exploration and understanding of THC-a. Let's keep the conversation vibrant and the information flowing!


